
Migrated from
East Slavs

Migrated
from
East Slavs
South
Slavs Serbs, Croats, Slovenes, and Macedonians (Bulgarians, of mixed
origin
like the Hungarians, speak a Slavic language)
The
Rus
South
Scandinavian/Nordic incursions (Varangians) – to
Germanic
influences
First
Articulations of Nationalism
Count
Sergey Uvarov
Head of St. Petersburg educational district under
Nicholas
I
3
Bases of Russian National Identity (1832)
orthodox Christianity
autocracy
narodnost (nationality) – belief
in Russian national superiority
Traditional elements of National Identity
Russian
Orthodox Church
czarism
nationalism
strong
connection
to the land, nature
Mother Russia
Earliest
Forms of State
1st
Eastern Slav state:
Prince
Svyatoslav
Son
Converts to Orthodox Christianity 988
Mongol
invasion 1223
Tatar
rule
Islam
Rise
of
14 Century – Rurikid Muscovy
Ivan
III (ruled 1462–1505)
“gathering of the Russian lands”
Romanov
Empire/Czarism
1600s-1917
Peter the Great (1689–1725)
Catherine the Great (1762-1796)
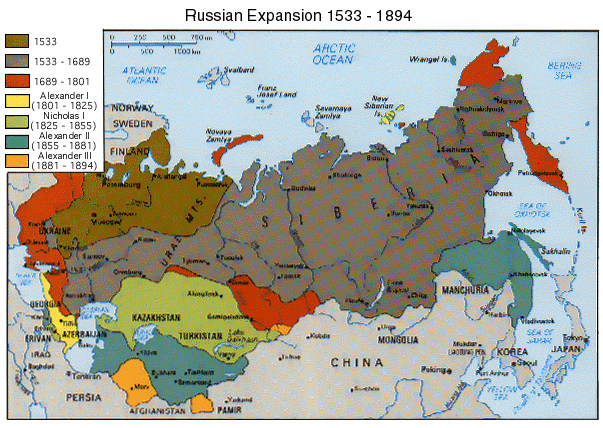
Civil
War (1918-1921)
Today
(2002 census)
Russian
79.8%
Tatar
3.8%
Ukrainian
2%
Bashkir
1.2%
other
or unspecified 12.1%
National
Extremists
Poland
Ethnic
Origins
W. Slavic tribe the polanie
pol means
field in Polish
reference to geography of Poland
Polish ethnic stock
Mixed
with Germanic tribes from the
W
E Slavs
from the Russia, Belarus,
Ukraine
Scandinavians (esp. Swedes) from the
N
1st
United State:
Mieszko I 966
converted to Christianity
Founds the Piast Dynasty
Major
competitors, invaders
Teutonic Knights
Tatars
Wladyslaw I reunites in 1320
Kazimierz the Great 1333-1370
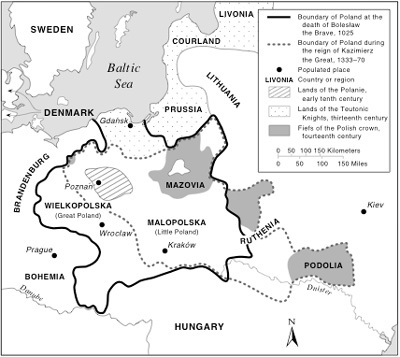
Jadwiga
marries Wladyslaw II Jagiello 1386
Jagiellonian Dynasty
Defeat
the Teutons at Battle of Tannenburg in 1410
16th Century
Commonwealth of Poland and Lithuania
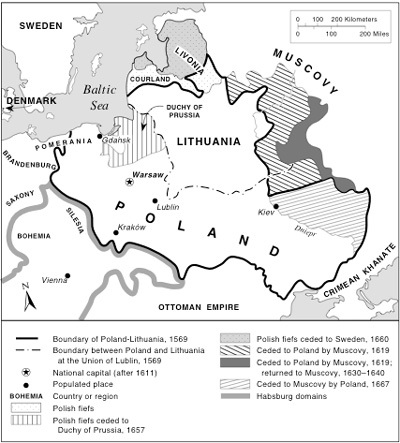
Noble
Republic 1572-1795
Elected Monarchy



First
Republic/Constitution May 3, 1791
Traditional
bases of National Identity
Catholicism, Marianism
Poland as Christ in Europe
nationalism (anti-Germanic, anti-Russian)
land (the Fatherland)
the Polish family
Today: