Xenophobia
and Islamophobia in Europe

Notes on
Raymond Taras’s book by the same name, 2013, Edinburgh University Press.
Critique of
book
Substance,
style, organization, argument, author’s point of view
Definitions
of Xenophobia, Islamophobia
Does Europe suffer from both?
Symptoms, Diagnosis,
Measurement
Xenophobia
Ethnic
hierarchies – favor northern, southern Europeans, then North Africans and
Asians, then Turks (78)
History of
“hospitality” toward foreigners as guests, BUT
Migrants
– indeterminancy, have over-stayed the conditions of hospitality
Asylum
– perhaps even more so as more or less permanent right to stay
Islamophobia
 Eurobarometer
Eurobarometer
Report
higher levels of racial tensions in countries with the strongest economies and
the highest concentrations of Muslims
EU15, >3%
Muslim, 40% report high religious tensions
New EU
states, <.1% Muslim, no significant religious tensions
Muslim
underclass (may overstate these differences but)
Higher rates
of unemployment, lower rates of education, lower incomes in UK, NE, FR, DE
(124)
Muslims DO
experience discrimination – in seeking work, in
Political
Questions Raised by the book
When did xenophobia become Islamophobia? How
much of Europe’s antipathy toward foreigners, migrants, etc., is xenophobia and
how much is Islamophobic?
Does it matter?
Is one more serious, more of
a threat to liberal order than the other?
His Argument
I. Prejudice is “natural” but need not turn
to racism
Other conditions need to be
met
Scarcity, competition,
self-interested motives
Cultural difference matters,
i.e., the degree of difference does increase the degree of prejudice against a
group
II. Conditions contributing
to rise of Xenophobia, Islamophobia in Europe

Structural variables:
Collision course between
labor shortages of 1960s (impact of WWII, smaller family sizes)
And 1970s economic downturn,
rise of OPEC, increased energy costs
Deindustrialization, economic
restructuring
Globalization, neo-liberalism
Normative variables:
Human rights revolution: UN Declaration of Rights, European
Convention on Human Rights
Commitment to protection of
refugees, right to asylum, right to family reunification makes Europe unable to
dampen down immigration as economic situation changes
Commitment by European
political elites to liberal values, human rights (guilt, atonement**)
*Out of step with European
publics, especially as deindustrialization proceeded apace in the 1990s
**This same rights revolution
led newer immigrant groups to demand recognition, rights that earlier groups
did not
e.g. right to “be different”
to maintain cultural community, language, religious
practices, other behaviors, symbols
assimilation now seen as cultural genocide
***free
speech and free exercise FOSTERS political Islam in ways not possible in
countries of origin
Political variables:
Decolonization
Pressures to absorb,
integrate post-colonial “subjects” and “citizens”
1968 UK Enoch Powell’s “rivers
of blood” speech
EU: laissez-faire on immigration,
subsidiarity
Member
states – various approaches to “integration”
“assimilation”
Multi-culturalism and corporatism (the Netherlands, Germany)
Integration
(through the workplace, schools) (UK)
Assimilation
(FR) – non-recognition of groups, group identities, Republicanism
End of Cold War,
disintegration of the Soviet empire, eventual enlargement of EU
Leads
to increased migration from the newer member states to the older
Inflames
already contentious situation
Result: rising right-wing
movements
National, cultural
defensiveness
Provocative Statements in
this book
Repeatedly endorses
Huntington’s “clash of civilizations” thesis
Is this overstating the
tension?
Can/should/must liberal
societies tolerate “intolerance”?
Be intolerant of those who do not subscribe specific tenets of
liberalism, e.g., Gender “equality,” same sex marriage
Belgian MEP speaks out against
Belgian Islamic Party
The Culture Wars in Europe

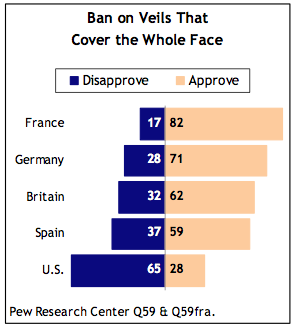
The veil – interpreted not as freedom of expression or religious
exercise for the individual but a VIOLATION of the norm of SECULARISM in the PUBLIC
SPHERE
Banned in Belgium, France
(in public places)
Law in Italy criminalizing
covering one’s face in public (masks and veils, need for public safety to
identify people)
Muslim council worker in
Belgium sacked
for not shaking hands with women
Europeans interpret this as
an affront to female citizens
Is it?
Should civil servants,
elected pols be required to have physical contact with consituents
of the opposite sex?
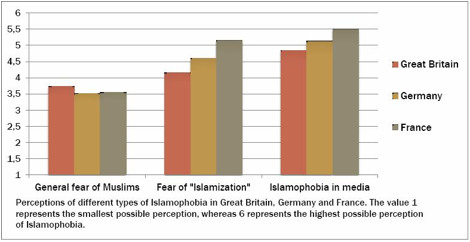
Role of Media in Inciting,
Perpetuating Islamophobia
Study
finds that European Muslims find most Islamophobia in
the media
See argument made at DesertPeace site