The New Europe
The Council of The European Union
Based on chapter by Jeffrey Lewis, in Michelle Cini and Nieves Perez-Solorzano Borragan, eds., 2010, European Union Politics, Oxford: Oxford UP.

Historically, has had been the EUÕs chief legislative body
Now, shares this role more with Parliament under the co-decision procedure in most policy areas
National
Interests
More than other EU institutions, clearly advocates of national interests
Why would this be the case?
Intergovernmentalism
Countries had veto, still have veto in areas of enlargement, revenue raising, defence, social security
But moving in direction of supranationalism
More things decided by Qualified Majority Voting (QMV):
For a decision to pass, it has to have a minimum of 255 votes out of 345.
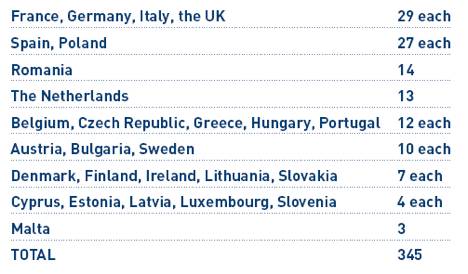
Germany 81.5 million citizens 1 vote/2.8 mln citizens
France 65.1 million citizens 1 vote/2.2 mln citizens
Spain 46.8 million citizens 1 vote/1.7 mln citizens
Poland 38.4 million citizens 1 vote/1.4 mln citizens
Belgium 10.4 million citizens 1 vote/866,667 citizens
Malta 408,000 citizens 1 vote/136,000 citizens
A majority of member states (in some cases two-thirds) must approve the decision
The votes cast in favor must represent at least 62% of the EU's total population
Lisbon Treaty Changes/Phase In:
QMV will be extended to 40 policy areas, including asylum, immigration, police co-operation and judicial co-operation in criminal matters
Double Majority Rule
55% of member states
65% of the EU's population
Phased in between 2014 and
2017
Organizational Hierarchy
European Council
Council of Ministers
Council of Permanent Representatives (COREPER)
Working groups (policy experts, fonctionnaires) (TOTAL: 40,000 people!! Lewis, 144)
**In reality, much more interconnected than this, variable from issue area to issue area
Council Configurations
Meetings are attended by whichever ministers are responsible for the items to be discussed:
General Affairs and External Relations (GAERC)
Foreign Ministers of Member States
General Affairs: multiple policy areas, e.g., enlargement, budget preparation
preparation for and follow-up to meetings of the European Council;
External Relations: foreign policy, defence, development aid
Economic and Financial Affairs (ECOFIN)
Finance Ministers
Justice and Home Affairs (JHA)
Employment, Social Policy, Health and Consumer Affairs (EPSCO)
Depends on issue; could be Justice Ministers, Interior Ministers, Ministers for Social Security, Health, etc.
Competitiveness
Transport, Telecommunications and Energy
Agriculture and Fisheries (AGFISH)
Environment
Education, Youth and Culture
Most meet several times a year; Education, Youth, Culture only twice per year
Council meetings are not public, filmed
Often Ministers are interviewed on their way into the building and give press conferences after the meetings