Poland
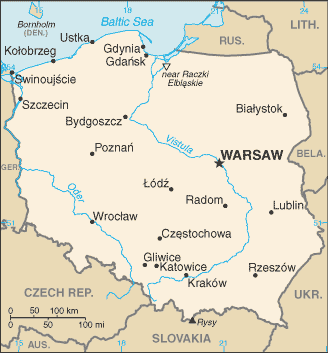

Geography
Location: Central
Europe, east of Germany
Area: 312,685 sq km
Area comparative: slightly smaller than New Mexico
Climate: temperate with cold, cloudy, moderately severe winters with frequent
precipitation; mild summers with frequent showers and thundershowers
Terrain: mostly flat plain; mountains along southern border
Natural Resources: coal, sulfur, copper, natural gas, silver, lead, salt,
amber, arable land
People
Population: 38,635,144
Age Structure: 0-14 years: 16.7%
15-64 years: 70.3%
65 years and over:
13%
Median Age: 36.43 years
Population Growth Rate: 0.03%
Birth Rate: 10.78 births/1,000 population
Death Rate: 10.01 deaths/1,000 population
Sex Ratio: at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female
total population: 0.94 male(s)/female
Life Expectancy at Birth: total population: 74.74 years
male: 70.71 years
female: 79.03 years
Ethnic Groups: Polish 96.7%, German 0.4%, Belarusian 0.1%, Ukrainian 0.1%,
other and unspecified 2.7%
Religions: Roman Catholic 89.8% (about 75% practicing), Eastern Orthodox 1.3%,
Protestant 0.3%, other 0.3%, unspecified 8.3%
Language: Polish 97.8%, other and unspecified 2.2%
Literacy: definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
99.8%
male: 99.8%
female: 99.7%
Economy
GDP (purchasing power
parity): $489.3 billion
GDP (official exchange rate): $249 billion
GDP - real growth rate: 3.3%
GDP - composition by sector: agriculture: 2.8%
industry: 31.7%
services: 65.5%
Labor Force: 17.1 million
Unemployment Rate: 18.3%
Population Below Poverty Level: 17%
Agriculture Products: potatoes, fruits, vegetables, wheat; poultry, eggs, pork,
dairy
Industries: machine building, iron and steel, coal mining, chemicals,
shipbuilding, food processing, glass, beverages, textiles
Slavs in Europe

Migrated
from Central Asia in 3rd or 2nd millenia BCE
East Slavs: Russians,
Ukrainians, and Belarussians
West Slavs: Poles,
Czechs, Slovaks, and Wends, or Sorbs
South Slavs: Serbs,
Croats, Slovenes, and Macedonians (Bulgarians, of mixed origin like the
Hungarians, speak a Slavic language)
Poland: Ethnic Origins
W. Slavic tribe
the polanie
pol means “field”
in Polish
reference to geography of Poland
Polish ethnic stock
Mixed with Germanic tribes from the W
E Slavs from the Russia, Belarus, Ukraine
Scandinavians (esp. Swedes) from the N
Peasant Culture
The Polish Peasant, Thomas and Znanecki
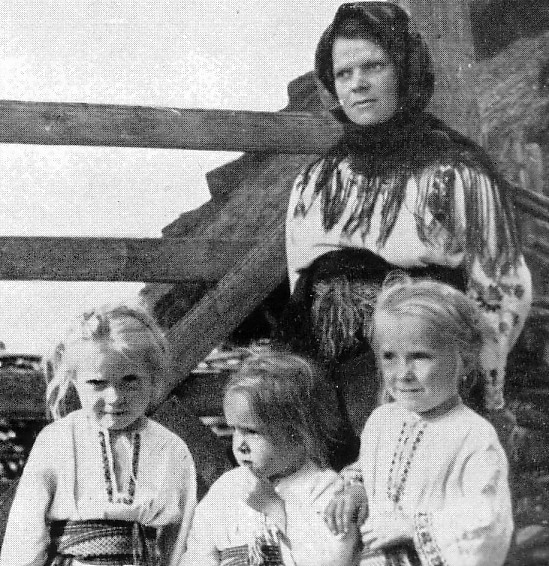

Characteristics of peasant
life
familial solidarity
absolute;
loyalty/assistance to family demanded by degree of relation
**husband/wife unit
marriage – not based on
love/sex/affection
rather RESPECT
their behaviors reflect
upon each other; do nothing that would lower the social standing of one
another’s families
e.g. shameful for wife to do hired
labor
dowry – received by the couple from both
sides
[still really the communal property of the
family because they are part of the family]
couple does not become individualized – a
new nucleus but forever tied to the larger family network
parental control/responsibility
LAND – SANCROSANCT
the means of family sustenance
father retires when son
becomes more able to manage the farm than he
patriarchy-boys more
important than girls – they get the land
pride = familial, not
individual
likewise
with shame
**collectivity/family group
identity
not indiv.
reinforced by village,
community
Is it appropriate to view
contemporary E Europeans in terms of peasant culture and sociology?
Did 50 years of communism
do nothing to changes these norms?

Polish Political
History
1st United
State:
Mieszko I 966
converted to Christianity (Catholicism)
Founds the Piast Dynasty
Major
competitors, invaders
Teutonic Knights
Tatars
Wladyslaw I reunites in 1320
Kazimierz the Great 1333-1370
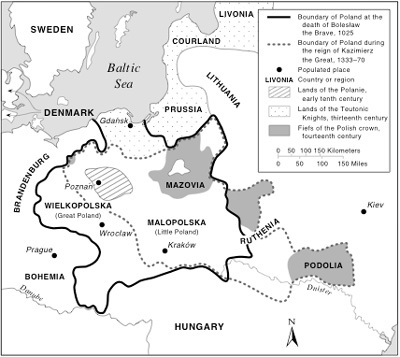
Jadwiga
marries Wladyslaw II Jagiello 1386
Jagiellonian Dynasty
Defeat the
Teutons at Battle of Tannenburg in 1410
16th Century
Commonwealth of Poland and Lithuania
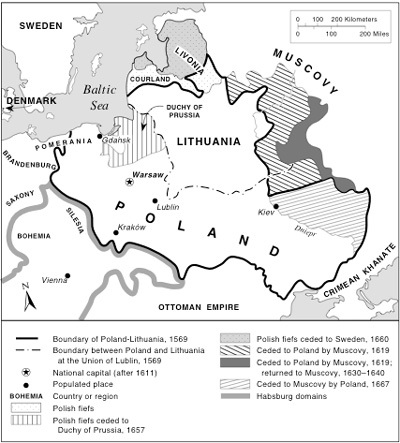
Noble
Republic 1572-1795
Elected Monarchy
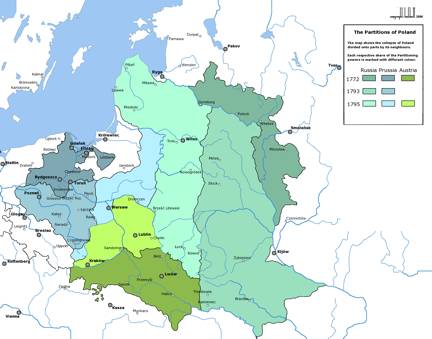
First
Republic/Constitution
May 3, 1791
The Second
Republic (1918-1939)
Interwar Period
General Pilsudski
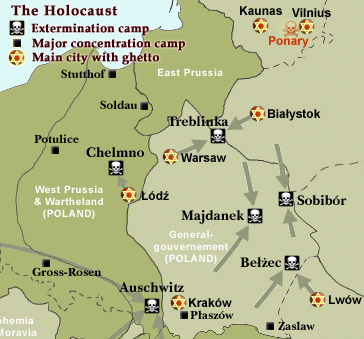
WWII
Molotov-Rippentrop Pact
Invasion September 17,
1939

Occupation by Nazis
Eastern Front
Holocaust
Communist
Period 1945-1989

Solidarity
Movement
Strikes, Gdansk
Shipyards
Lech Walesa

Pope John
Paul II


Legacies of
Communism

Traditional
bases of National Identity
Catholicism, Marianism

Our Lady
of Czestochowa (The Black Madonna)
Poland as Christ in Europe
nationalism (anti-Germanic, anti-Russian)
land (the Fatherland)
the Polish family
Today
Post-Communist
trend toward nationalism/racism/anti-foreigner sentiments
Government
Government Type: Republic
Capital: Warsaw (pictured below)

Legal System: mixture of Continental (Napoleonic) civil law and holdover
Communist legal theory; changes being gradually introduced as part of broader
democratization process; limited judicial review of legislative acts, but
rulings of the Constitutional Tribunal are final; court decisions can be appealed
to the European Court of Justice in Strasbourg
Dual Executive
President and Prime Minister each have executive powers
like French system
President directly elected
2 ballot election
has power to sign treaties, control armed forces, must sign bills into law
The Executive Branch
Chief of State: President
Lech KACZYNSKI (PiS)

Office
of the President’s Website
Head of Government: Prime Minister Donald Tusk (PO)

Cabinet: Council of Ministers responsible to the prime minister and
the Sejm
The Legislative Branch
Bicameral legislature consisting of
Upper House
The Senate(Senat)
100 seats
members are elected by a majority vote on a provincial basis to serve four-year
terms
Lower House
The Sejm
460 seats
members are elected under a complex system of proportional representation to
serve four-year terms
5% threshhold (except for German minority)
Results of 2006
elections % Seats
Law and Justice
(PiS)
27 % 155
Civic Platform
(PO)
24% 133
Self-defence
(Samoobrona)
11% 56
Democratic Left Alliance (SLD)
11% 55
League of Polish Families
(LPR) 8% 34
Polish Peasant Party
(PSL)
7% 25
The German
minority
2
Government Coalition between the PiS and PO
Law and Justice Party
right wing party
former AWS and ROP members
traditional, Euroskeptic, populist
social policies based on Catholic Church
anti-communist
pro "lustration" but
Economically, leftist
state-guaranteed minimum social
safety-net
intervention of the state into economic
issues
proposes two personal tax rates (18% and
32%)
tax rebates related to the number of
children in a family
reduction of the VAT rate
privatisation with the exclusion of
several dozen state companies
of strategic importance for the country
PiS opposes cutting social welfare
spending
proposes the introduction of a system of
state-guaranteed housing loan
Politically
for centralizing power - removing
governing bodies over media, monetary policy
giving president decree powers
pro-EU and keeping Polish forces in Iraq for one more year (since
election)
Civic
Platform center-right
coalition of post-Solidarity party (AWS)
Freedom Union (UW) (center liberal party)
Freedom Union
liberal party
(merger of former Democratic Union and Liberal-Democratic
Congress)
individual liberty, centrist, pro EU integration
rapid privatization
former Foreign Minister Bronislaw Geremek
Democratic Left Alliance (SLD)
post communist successor party
former two-term president Aleksander Kwasniewski
![]()
and former PM Wlodimierz Cimosewicz
The Judicial Branch
Supreme Court (judges are appointed by the president on the recommendation of
the National Council of the Judiciary for an indefinite period)
Constitutional Tribunal (judges are chosen by the Sejm for nine-year terms)