Comparative
European Politics
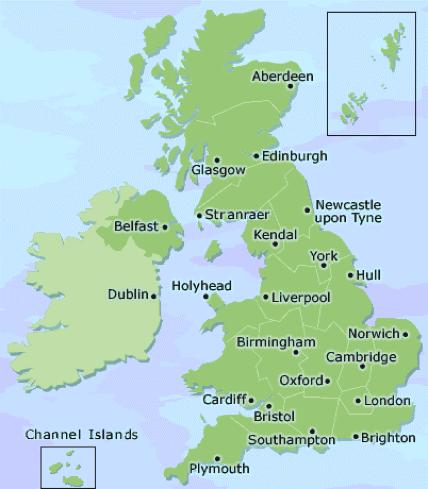
The United Kingdom
Geography



Political Context, Culture,
History
Four nations/nomenclature
Conventional Wisdom on UK
was to emphasize its
Homogeneity, integration, political stability, consensus politics
Resilience of its political institutions, their ability to foster
compromise
What has happened in the
world and in the academy to change this view???
Post-Colonial
struggles since WWII – resulting in
Increased Ethnic/National Consciousness
Decline of UK/Europe and Ascendancy of US/SU
New Waves of Immigration – increased diversity in UK
Decline of Britain in the ‘70s “the sick man of Europe”
“The Troubles”

BBC story on Orangemen
Ethnic Make-up of
Contemporary UK (2001
census; source: CIA World
Factbook, August 16, 2009)
White 92.1%
English
83.6%,
Scottish 8.6%, Welsh 4.9%, Northern Irish 2.9%
Black 2%
Indian 1.8%
Pakistani
1.3%
Mixed 1.2%
Other 1.6%
Religous
Affiliations (2001
Census; cited in the CIA World Factbook, August 16, 2009):
Christian (Anglican, Roman Catholic, Presbyterian,
Methodist) 71.6%,
Muslim
2.7%, Hindu 1%, other 1.6%, unspecified or none 23.1%
Political Reform in
Response to Regionalism/Nationalism: Devolution
New parliaments in
Scotland, Wales
Political Culture
Traditionally modern, modernly traditional
Pragmatism – change, innovation inevitable, good
(W. belief in PROGRESS***)
Deference to authority
Class politics
English much more class conscious than Americans
Class distinctions much
more important
Why???
History, institutions, education system, party manifestations of
Oratory, Debate, Humour, Satire

The UK in the WORLD and in
EUROPE
How to characterize UK’s position in the world
Complex – colonial power, imperialism

People
adventuresome, embrace opportunity to “experience” other cultures, peoples
Yet in
Europe – often aspires to be “isolationist”
What role has UK played
in European integration via EU??
Generally a “Euroskeptic”
Foot dragger
Only joined
EECs in 1973
after first advisory
referendum in UK history
blackballed twice by de
Gaulle
in fact, initiated
competitor to European Communities called
the European Free Trade
Area – soley free trade
Conservative
Party would continue along these lines but
Labour Party, under
Blair at least, much more pro-Europe
Signed onto
to Social Charter (finally) in Treaty of Amsterdam (1997)
Plans to join the Euro in 2004
or so
Comparative European Politics
The UK
Institutions, Power and
Politics

The Westminster Model –
Britain’s Greatest Export
Characteristics of:

Monarchy - Constitutional
limits on power of monarchy

Parliamentary sovereignty
No judicial review
No Bill of Rights til recently
No single written constitutional document
Who has power?
Prime Minister

primus inter pares – less so today – more shared responsibility
how selected
Cabinet ministers
Differences between UK and
American cabinet members
British members are also members
of Parliament – expected to spend considerable time there and in home district
Selected for their
popularity and political skill vs. in US???
Differences in Accountability between UK/US cabinets/governments
Question Hour

Labour
Party Front Bench
Conservative
Party Front Bench
Lib-Dems
Front Bench
House of Commons (lower
house)

646 members
~ 5 year terms
ruling party decides when to call for elections
Last election: May 5,
2005
Labor 35.2%
Conservative 32.3%
Liberal Democrats 22%
other 10.5%
Labor 356
Conservative 197
Liberal Democrat 62
other 31
Differences between UK MPs
vs. US members of Congress
Brits make less ($75,000 or so compared to over $100,000 in US)
Have less staff, office space – one part time assistant, shared offices
the norm –
Compared to US:
Brits represent fewer constits – 659 members of House of Commons ~ about 90,000
constits per seat (compared to 550,000 in US)
House of Lords (upper
house)

no elections
500 life peers
92 hereditary peers
1999 - House of Lords Act
elections were held in the House of Lords to determine the 92 hereditary peers
who would remain there
elections are held only as vacancies in the hereditary peerage arise
Contemporary Changes in Westminster Model
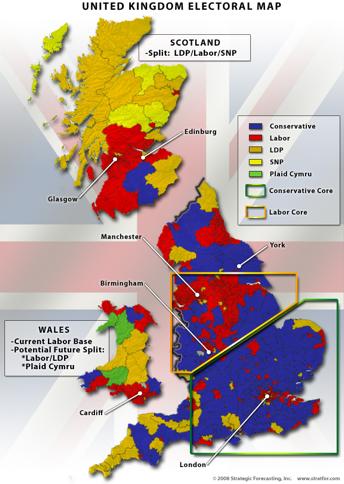
Devolution
regional parliaments in Scotland and Wales
homerule restored in Northern Ireland (suspended as of 2002)
directly elected mayors
Bill of Rights
Reform of House of Lords
Other differences with US
system
Corporatism – role of interest groups, advisory bds, QUANGOs
Link between Labour
Party and Trade Union Congress
Distribution of seats
by region – over-rep of Celtic Fringe (58)
Party Politics
Conservative Party
Roots
Ideology
Constituencies
Geographic Strengths
Thatcherism
1990s decline
Labour Party
Roots
Ideology
Constituencies
Geographic Strengths
Blair and “New
Labour”
The Third Way
Liberals as “the center” in
Euro politics
Business, libertarian,
“radicals”
Other Parties
Scottish National Party
Welsh
Nationalist Party/Plaid Cymru
British National Party
The Green Party
Northern Irish Party
Democratic Unionist Party
Sinn Fein
Social Democratic and Labour
Party
UK Parliamentary Elections
1997 election
Overall Vote Percentages:
Labor 35.2%
Conservative 32.3%
Liberal Democrats 22%
other 10.5%
Seats:
Labor 356
Conservative 197
Liberal Democrat 62
other 31