Mao Tse Tung

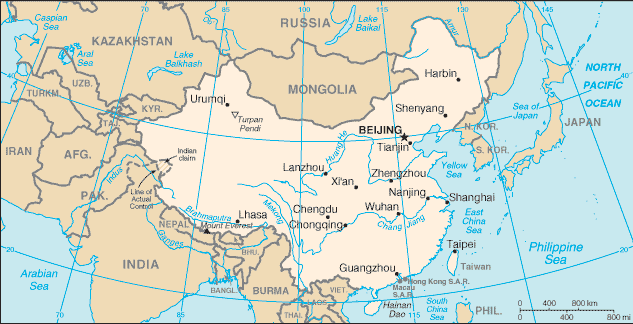
Overview (Source:
CIA World Factbook)
Geography:
3rd Largest country in the world
Climate: varied; everything from tropical to subarctic
Terrain: mountains, high plateaus, deserts in west;
plains, deltas, and hills in east
Natural Resources:
coal, iron ore, petroleum, natural gas, mercury, tin, tungsten,
antimony, manganese, molybdenum, vanadium, magnetite, aluminum, lead,
zinc, uranium, hydropower potential (world's largest)
People:
Most populous country in the world: 1.3 bln
Fertility Rate: 1.72
births per woman (2005 est.)
Sex Ratio at birth: 1.12 males per female
Ethnic groups:
91.9% Han
8.1% Zhuang, Uygar, Hui, Tibetan, Miao, Manchu, Mongol, Buyi, Korean
and others
Religion:
Taoist, Buddhist, Muslim 1-2%
Christian 3-4%
Officially atheist
Economy:
GDP: $8.158 trilliion (ppp)
GDP growth: 9.2% (2005 est.)
GDP per capita: $6200 (ppp)
GDP generated by sector:
AGriculture 14%
Industry 52%
Service 32.5%
Employment by sector:
Agriculture 49%
Industry 22%
Service 29%
Unemployment:
Urban 4.2%
Rural 20%
Pre-Modern Political
History
"Oriental despotism"
Ancient political
dynasties
Feudalism, fragmentation during:
Xia Dynasty
2200-1700 BCE
Zhou dynasty 770-256 BCE
produced K'ung Fu-tzu (Confucius)
and Laozi (Lao-tzu)
Qin Dynasty
475-221 emerges
First Qin Emperor 221-210 BCE
system of prefectures, counties under central control
intensive agriculture
irrigation systems
begin work of Great Wall
Han Dynasty 206
BCE-220 CE
break up into
three kingdoms
Reunited in 581
under Sui Dynasty
Tang Dynasty
618-907
zenith as cultural and commercial center of Asia
Song Dynasty
960-1279
literature, philosophy, sciences flourish
moveable type, gunpowder, magnetic compass
Mongol and Tatar
invasions
Subjugation under
Genghis Khan 1155-1227
Kublai Khan
(1279-1294)
Great Canal completed
left Chinese culture and technology in place,
allowed to flourish
Ming Dynasty
1368-1644
moves capital to Beijing
Manchus
adopted Chinese form of administration, laws, culture
empire 300 mln
included China, Manchuria, Mongolia, Tibet, Taiwan, Turkestan
Foreign Relations
Negative Experiences with West
Europeans
"discover" China
Portuguese 1516
then Spanish, Dutch, English
Only allowed into Guangzhou (port) for trade, restricted
British forced opium trade
into China
led to Opium War 1839-1842
China lost
forced in Treaty of Nanking to open five seaports and to cede Hong Kong
to UK (til 1999)
Weakened
1898 Europeans "leased" major
ports
Lost territory to Russia, Japan
1900 Boxer Rebellion
anti-foreign rebellion
crushed by intervention of British, French, German, American, Russian
and Japanese forces
1911 Manchu dynasty falls
Brief republic Sun Yat-sen
consolidated th Kuomintang (KMT - the Nationalist
Party)
On winning side in WWI but
not rewarded at Versailles
Then strongman Yuan Shikai
dies in 1916
Warlords rule
Civil War
between the KMT and the Communists through 1949
KMT led by Chiang Kai-shek
the Communists led by Mao
Zedong (Mao Tse Tung)
1934-35 Mao's "Long March" a
retreat into the mountains of Yenan
Manchuria (Chinese industrial
heartland)
became Manchukuo
Japanese puppet state 1932
– WWII
Japan defeated in WWII
forced out of China
Civil War reignites
Communists drive the KMT off
mainland China to Formosa, now Taiwan
October 1, 1949 - People's
Republic of China founded
Maoism
Mao Tse Tung

Marxism in some ways
"class struggle, class struggle, class struggle"
but with Maoist, Chinese twist
human will can overcome all material obstacles
peasants as the engine of revolution
Revolution's goal to "harness the hurrican force of
the people" and
Prevent privileged elite from emerging
e.g. re-education camps for
bureacrats
communal living
The Great Leap Forward
1958
futile attempt to industrialize the countryside
1960-1962
industrial production actually shrank
famine; millions starved
The Cultural Revolution
1966
The Red Guards (later condemned)
Mao's little red book

party leadership
purged
intellectuals persecuted
entire education
system shut down
2 mln people died
as result of the Cultural Revolution
BBC
Site of Images of Cultural Revolution
Deng Xiaoping
“to be get rich is glorious”

It doesn’t matter the color of the cat as long as it catches the mouse
Why has China been able to reform economically without the whole system collapsing as happened in the Soviet Union?
Because Chinese Communism has
always been
more pragmatic, less idealistic.
Roots as a guerilla movement - need to
be flexible, decentralized, allow for innovation.
Two sayings (again from Deng):
Seek Truth from Facts.
Practice is the Only Test for Truth.
1979-Present = period of reform
Conditions leading to reform:
1) Economy in disarray by end of ‘70s
a. result of
inefficiencies of command economy and
b. Cultural Revolution
- schools closed, no engineers/teachers produced for 10 yrs
therefore, lagged
behind
the West in technology
2) Continuity and Confidence of Chinese
leadership
reforms initiated by the
creators of the system
can’t argue with them
especially Deng Xiaoping
(aided by new generation of reformers)
Three types of Economic
Reforms
1) decollectived agriculture - household
responsibility program
meet state production
goal then can sell rest for profit
now China can actually
export food!!
2) rural enterprises (TVEs -
Township and
Village Enterprises)
local government run
businesses for profit and
cooperatives (where
all town residents own shares)
grass-roots
entrepreneurism
- outdoor markets
3) trade and foreign
investment
Special Economic Zones
- joint ventures between foreign capital and Chinese
Other reforms:
Allow lots of Chinese students to study
in the West (new ideas back to China)
Temples reopened
Travel possible within China
Access to Foreign Media (TV)
Local Elections
Political Rule
unreformed
"dual rule" 1956
state organs responsible to next higher level of state adminstration
AND to the part organization on the same level
See Magstadt,
Table 8.2 p.309
General Secretary
Hu Jintao

Premier Wen Jiabao

Democratization
Pressures in China
Challenges from Student
movement (Tiannemen
Square), Falun Gong
Amnesty
International Report on China
Amnesty
International Story on Abortion Protester
Amnesty
International