People and Politics Worldwide
India
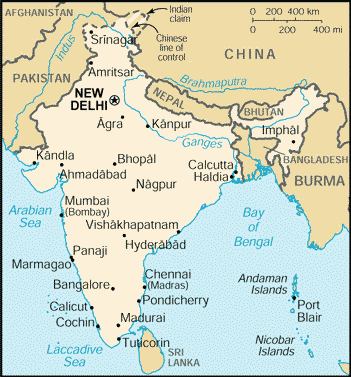
Source of
map and statistics: CIA World Factbook
Geography
Location: Southern
Asia, bordering the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal, between Burma and
Pakistan
Area: total: 3,287,590 sq km
Area Comparative: slightly more than one-third the size of the US
Climate: varies from tropical monsoon in south to temperate in north
Terrain: upland plain (Deccan Plateau) in south, flat to rolling plain along
the Ganges, deserts in west, Himalayas in north
Natural
Resources: coal (fourth-largest reserves in the world), iron ore, manganese,
mica, bauxite, titanium ore, chromite, natural gas, diamonds, petroleum,
limestone, arable land
Natural Hazards: droughts; flash floods, as well as widespread and destructive
flooding from monsoonal rains; severe thunderstorms; earthquakes
Enviroment Current Issues: deforestation; soil erosion; overgrazing;
desertification; air pollution from industrial effluents and vehicle emissions;
water pollution from raw sewage and runoff of agricultural pesticides; tap
water is not potable throughout the country; huge and growing population is
overstraining natural resources
People
Population: 1,080,264,388
Age Structure: 0-14 years: 31.2%
15-64 years: 63.9%
65
years and over: 4.9%
Median Age: 24.66 years
Birth Rate: 22.32 births/1,000 population
Death Rate: 8.28 deaths/1,000 population
Sex Ratio: 1.06 male(s)/female
Life Expentancy at Birth: total population: 64.35 years
male:
63.57 years
female:
65.16 years
Ethnic Groups: Indo-Aryan 72%, Dravidian 25%, Mongoloid and other 3%
Religions: Hindu 80.5%, Muslim 13.4%, Christian 2.3%, Sikh 1.9%, other 1.8%,
unspecified 0.1%
Languages: English enjoys associate status but is the most important language
for national, political, and commercial communication; Hindi is the national
language and primary tongue of 30% of the people; there are 14 other official
languages
Literacy: definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 59.5%
male: 70.2%
female: 48.3%
Government
Government
Type: federal republic
Capital: New Delhi
Independence: 15 August 1947 (from UK)
Legal System: based on English common law; limited judicial review of
legislative acts; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction, with reservations;
separate personal law codes apply to Muslims, Christians, and Hindus
Economy
GDP
(purchasing power parity): $3.678 trillion
GDP (official exchange rate): $735.6 billion
GDP - real growth rate: 7.1%
Labor Force: 496.4 million
Labor Force by Occupation: agriculture 60%, industry 17%, services 23%
Unemployment Rate: 9%
Population below poverty level: 25%
Inflation Rate: 4.4%
Agriculture products: rice, wheat, oilseed, cotton, jute, tea, sugarcane,
potatoes; cattle, water buffalo, sheep, goats, poultry; fish
Industries: textiles, chemicals, food processing, steel, transportation
equipment, cement, mining, petroleum, machinery, software
Political
History
long history
of permanent settlement, advanced civilizations rooted in the Indus Valley more
that 2400 BCE
many long
lasting empires
alternating
between Hindu and Muslim control
Mauraya Empire (Hindu)
Ashoka (273-232 BCE) unites all of India
converted to Buddhism
art, architecture flourish
but after his rule, reverted to mostly Hindu kingdoms
Muslim rule 13th
C
Pinnacle in 16th C Moguls
Babur, Akbar, others
Taj Majal
18th Century
British colony
first under British East India Company until Sepoy Mutiny 1857-1859
Then by British
crown directly until 1947
Political
Culture
Influences of Hinduism
karma, reincarnation, caste
tendency to withdraw into world of ritual, dharma, belief
that life is miserable
Ethno-religious
complexity
Muslims,
Sikhs - deeply divided society
Village as organizing social unit
“own” land in common
elders rule
Conservative,
Hierarchical Social Structure
Caste System
Brahmin -
priests and scholars
Kshatriya - warriors and rulers
Vaisya - artisans, shopkeepers, farmers
Sudra - farm laborers, menial workers
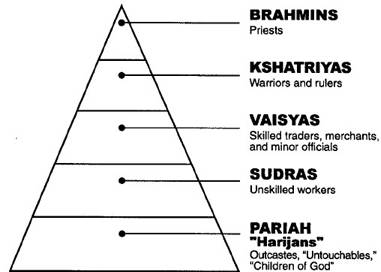
"unscheduled castes" below caste
the "untouchables"
Dalits - slaughter animals, handle waste (animal and human)
Discrimination based on caste made unconstitutional in 1965
but still exists, people still marry within caste, subcaste
Gandhi
Mohatma/Mohandas
b. October 2, 1869
assasinated January 30,1948
by Hindu nationalist/extremist Nathuram Godse

Gandhi
educated to be a lawyer in England
South Africa experience
Returns to India
transformed!!
dressed as
common laborer not fancy gentleman
Homespun - cloth
spun and woven trad’lly not in England; with Brit tech
Gandhi’s
Tactics
Civil
disobedience
- disobeying
unjust laws
Nonviolence
- turning
the other cheek
- his interp of
Christ’s teaching
command to
challenge injustice/barbarism to make a pt
- force moral
tension in violent perpetrator - make him feel your humanity
Not all in
India were able to live according to his tactics
Fighting between
Hindus and Muslims allows Brit to continually divide and conquer
Can’t never
agree on what kind of state
So independence
struggle drags on
1920 (when
Gandhi becomes leader of Indian National Congress)
til 1947 when
partition agreed
Lord
Mountbatten - Gov Gen of India
Jawaharlal
Nehru - leader of Indian National Congress
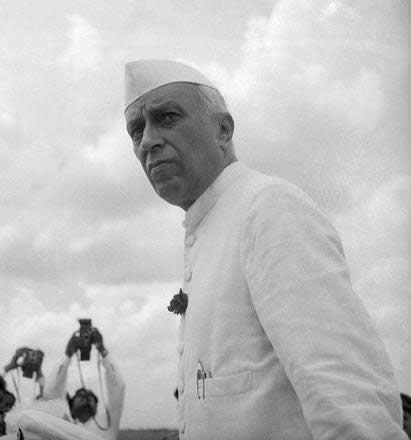

Nehru
becomes PM of India
and Liaquat
Ali Khan PM of Pakistan
Massive
population relocations
Still dispute
over Kashmir
Elite - Hindu choose to be part of India
but Muslim majority want to be part of Pakistan
India’s
Ethnic Complexity
800 languages,
incl 60 non-Indian languages
Largest language
groups:
Hindi
38%
Urdu,
Punjabi 10% each
Dravidian
languages 22%
Official
Languages Act 1965 to permit English, regional languages (education)
Parliamentary
System
House of the
People - Lok Sabha

542 members - elected from SMD
5-yr
terms (confidence)
vote
of censure can be introduced by 50 members
Head of
government: Prime Minister Manmohan SINGH (since 22 May 2004) 
Cabinet: appointed by the president on the recommendation of the prime minister
Council of
States - Rajya Sabha
250 members
president
appoints 12 to represent professions and arts, others elected by state
legislatures
Legis goes back
and forth til agree - or joint session held - majority vote taken;
Judicial Branch:
Supreme Court (one chief justice and 25 associate justices are appointed by the
president and remain in office until they reach the age of 65 or are removed
for "proved misbehavior")
Differences
from British System
Supreme Court -
judicial review
Federalism
President -
Symbol of national unity
5-yr term
elected by
electoral college comprising members of Parliament and state legislatures
(states on parity basis)
appoints PM and cabinet (on PMs recommendation
President now:
President A.P.J. Abdul KALAM (since 26 July 2002)

Parties
The Congress
Party -
controlled
parliament for 45 yrs
party
of Gandhi, Nehru
Indira
Gandhi

son Rajiv

both assassinated while PM;
Sonia Gandhi,Rajiv’s wife

party leader at
election time, but refused PM post
BBC Story on Nehru-Gandhi Dynasty
Congress Party
Mildly left of center
Supports
Democratic-Socialism
Nationalization
of key sectors (banking, steel industry) without alienating business
Non-alignment in
foreign affairs (FSU)
Corruption
problems;
1998
elections won 31%
Bharatiya
Janata Party (BJP)
Largest vote
getter in 1998 elections
47% -
PM Atal Bihari Vajpayee

Combination of
Hindu nationalism (anti-Muslim; stress religious ritual, connection)
and
middle-class appeal (shop owners, artisans)
deregulation of
economy, infusion of foreign capital
2004
Elections
Congress wins
but Sonia Gandhi refuses to take PM spot
Manmohan Singh
chosen
Sikh born in
West Punjab
educated at
Oxford and Cambridge
former International Monetary Fund official
former governor of India's Central Bank
the architect of India's economic reform
Deregulation
Privatization
FDI
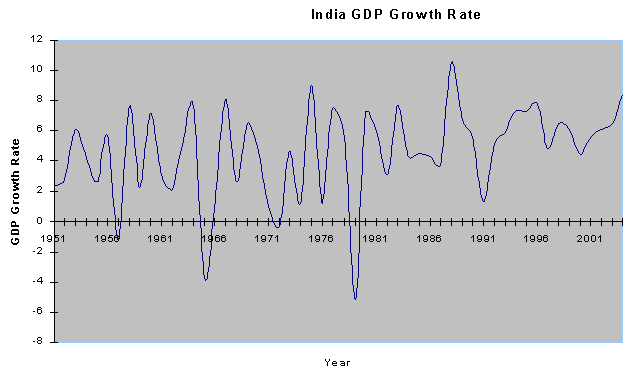
India's
Post-Industrial Economy
India's
Growth
Bangalore
Outsourcing
Growth
Indian Firms in
Competition to Acquire Rover, Jaguar
Hooray for Bollywood!
