Israel


Geography
Location: Middle East, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, between Egypt and
Lebanon
Area: total: 20,770 sq km
Area Comparative: slightly smaller than New Jersey
Climate: temperate; hot and dry in southern and eastern desert areas
Terrain: Negev desert in the south; low coastal plain; central mountains;
Jordan Rift Valley
Natural Resources: timber, potash, copper ore, natural gas, phosphate rock,
magnesium bromide, clays, sand
People
Population: 6,352,117
Age Structure: 0-14 years: 26.3% (male 855,054/female 815,619)
15-64 years: 63.9% (male 2,044,135/female 2,016,647)
65 years and over: 9.8%
Median Age: total: 29.6 years
male: 28.8 years
female: 30.5 years
Population Growth Rate: 1.18%
Birth rate: 17.97 births/1,000 population
Death rate: 6.18 deaths/1,000 population
Sex Ratio: at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.75 male(s)/female
total population: 0.99 male(s)/female
Life Expectancy at birth: total population: 79.46 years
male: 77.33 years
female: 81.7 years
Ethnic Groups: Jewish 80.1%
Europe/America-born 32.1%
Israel-born 20.8%
Africa-born 14.6%
Asia-born 12.6%
Non-Jewish
19.9% (mostly Arab)
Religions:
Jewish 76.5%
Muslim 15.9%
Arab
Christians 1.7%
other
Christian 0.4%
Druze
1.6%
unspecified
3.9%
Languages:
Hebrew (official), Arabic used officially for Arab minority, English most
commonly used foreign language
Literacy:
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 95.4%
male: 97.3%
female: 93.6%
Economics
GDP - per capita (PPP): $22,300
GDP - real growth rate: 4.7%
GDP - composition by sector: agriculture: 2.8%
industry: 37.7%
services: 59.5%
Labor
force: 2.42 million
Labor force by occupation: agriculture, forestry, and fishing 2.6%,
manufacturing 20.2%, construction 7.5%, commerce 12.8%, transport, storage, and
communications 6.2%, finance and business 13.1%, personal and other services
6.4%, public services 31.2%
Unemployment
rate: 8.9%
Population below poverty line: 21%
Consumption by lowest 10%: 2.4%
Consumtion by highest 10%: 28.3%
GINI coefficient: 35.5
Female Labor Force Participation: 41%

Economic model
mixed, socialist elements
Moshav, moshavim
families own separate farms but cooperate in many aspects of agricultural
production and marketing.
Kibbutz,
kibbutzim
all property owned collectively
Agriculture
products: citrus, vegetables, cotton; beef, poultry, dairy products
Industries: high-technology projects (including aviation, communications,
computer-aided design and manufactures, medical electronics, fiber optics),
wood and paper products, potash and phosphates, food, beverages, and tobacco,
caustic soda, cement, construction, metals products, chemical products,
plastics, diamond cutting, textiles, footwear
History
Founded 1948
“under extreme duress” (Magstadt, 464) when British mandate over Palestine
(est’d after WWI; granted by League of Nations) formally expired.
Why founded
then?
Precarious
Geography, Conflictual 20th C History
Surrounded
by Arab states hostile toward the idea of Jewish state/Zionism
Bordered by
Egypt, Lebanon, Syria, Jordan and the Mediterranean)
Started about
size of NJ but then gained territory via several wars
British had
requested both a Jewish state and an Arab state in Palestine w/Jerusalem
designated an international city (which it was until the 1967 war w/UN
administration)
Arabs rejected
this idea; Zionists accepted.
Led to first
Arab-Israeli war – May 15, 1948 starts - lasted 8 mos.
Egypt,
Transjordan, Lebanon, Iraq fought against Israel
Drove nearly
1 mln Arabs from their homes-roughly 70 of the Arabs living in Palestine; they
fled to surrounding countries, Arab-occupied parts of Palestine
Israel wins
gaining 30% more territory than originally granted by the UN; Israel claims it
won the land “fair and square” and that they original UN resolution on
Palestine is invalid because it was invaded; also has ignored subsequent
UN resolution giving Palestinians a right to return to their homes or to be
compensated for losing them
2nd Arab-Israeli
War 1956 Suez Crisis (decolonization of Suez – Britain pulls out – Nasser
nationalizes the canal for Egypt)
UN occupies
with Emergency Force (Egypt humiliated)
Leads to 3rd
Arab-Israeli War – 1967 –
The Six Day
War – Israel defeats both Egypt and Syria – seizing from them and from Jordan
Sinai peninsula, West Bank, Gaza Strip, East Jerusalem, and the Golan Heights –
these are what the Palestinians call the “occupied territories” today
Control over
Jerusalem an “insoluable” issue since
1973 Yom Kippur
War
1983 War in
Lebanon
1989-91 –
1st Intifada (Palestinian uprising)
2000 – 2nd
Intifada
2002 – 3rd
Intifada?
US support, arms
sales, role in region
Law of Return
all Jewish
immigrants welcome with open arms
Pop. 1948 –
900,000; doubled by 1955
Cultural
mix/tensions in Israel
Sephardic
Jews – from Spain, Portugal, Middle East
Ashkenazic Jews
– from CE Europe – the mainlstay of the Zionist movement
Today – new
influxes of Jews from former Soviet Union, esp. Russia
Israel has much
to be proud of:
especially
its democratic system
Magstadt states
“Israel
has accomplished its original aims of providing a homeland and a safe haven for
all Hews. It has built a strong state capable of defending itself against
its enemies (Arabs) (sic), who greatly outnumber its own Jewish
population. It has also built a modern economy and given its people a
decent standard of living – tone that can only be envied by its Arab
neighbors. It has done all of this in spite of its neighbors’
hostility. The political system has functioned as a parliamentary
democracy despite the constant threat of terrorist attacks and frequent
national emergencies. Elections are held regularly, and all adults (including
Israeli Arabs) have the right to vote. Opposition and dissent are
protected by law, although Palestinians deemed to post a threat to Israeli
society are arrested and imprisoned" (Magstadt, 502)
Israel’s
Political System
Government
Type: parliamentary democracy
no written constitution
Capital: Jerusalem;
note - Israel
proclaimed Jerusalem as its capital in 1950, but the US, like nearly all other
countries, maintains its Embassy in Tel Aviv
Legal System: mixture of English common law, British Mandate regulations, and,
in personal matters, Jewish, Christian, and Muslim legal systems; in December
1985, Israel informed the UN Secretariat that it would no longer accept
compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
Executive Branch

Chief of state: President Moshe KATZAV
![]()
Head of government: Prime Minister Ariel SHARON ; note - Prime Minister
(Acting) Ehud OLMERT
Cabinet: Cabinet selected by prime minister and approved by the Knesset
Legislative
Branch
Israeli
Parliament is called the Knesset

Unicameral
120 seats; proportional representation (coalition and minority governments the
norm)
four-year terms
2006 Election
Results
Judicial Branch
Supreme Court (justices appointed for life by the president)
Parliamentary, multi-party democracy
Major parties
The Likud Party (conservative, center-right)
Leader was Ariel Sharon (split to found Kadima Party Nov. 2005)
The Labour Party
(center-left)]
Leader Amram Mitzna
Story on Labour Party
Story on Political Parties 2006
Kadima
founded by Sharon in Nov. 2005; narrow election victory in 2006 despite Sharon
being in a coma
centrist
attempt to bring together left and right
Shinnui (Change)
liberal democratic party
Arab Parties
The Palestinian
Question
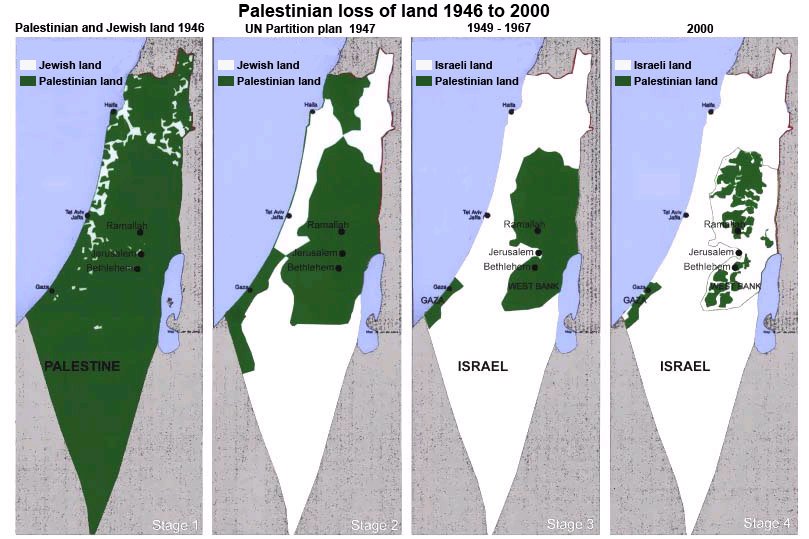
Major cleavage
in Israeli politics
1st PM/Defense Minister– David Ben Gurion (from Poland)
Other PM “hardliners”
Golda Meir, Moshe Dayan, Menachem Begin (who won Nobel Prize for Camp David
Accords with Egyptian President Anwar al-Sadat negotiated by then President
Jimmy Carter-1979)Yitzhak Shamir, and now, Shimon Peres
vs.
Moderates
Ariel Sharon?
current prime
minister (2005)
forming new centrist party
The Intifada
Palestine Liberation Organization

The Palestinian
Authority
