Western European Politics
The European
Union: A Vehicle for European Unity


Why Europe? Why now?
European History
clash of
religious/cultural/political ideas and
economic interests
Culminates in the two World Wars
The end of history?
Fukayama, 1989
for W
Europe the choice comes sooner
begins
the 1950s
process lasts through the end of the 20th Century
Europe's ideological choice
not US model
not Communism
Third way:
social democracy
EU
1. as recognition of this political,
cultural convergence
2. as Europe's conscious choice for peace
3. as a vehicle for economic
restructuring
and the consolidation
of Europe's economy
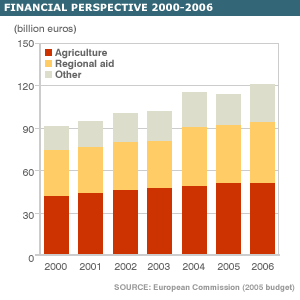
efficiencies in
agricultural production*
regional aid,
investment*
capital investment,
e.g. Airbus
labor markets
prices, consumer
choices
4. as a counterweight to American hegemony
both economically and
politically in international affairs
History of the European
Union
1951 - Treaty of Paris
European Coal and Steel
Community (ECSC)

Purpose: to reduce economic
(and, hence, military) competition in coal and steel industries among original
six members by forming a customs union for coal and steel.
Original six - France,
Germany, Italy, Belgium, Netherlands, Luxembourg (collectively referred to as
the BENELUX countries)
1957 - Treaty of Rome
Est’d European Economic
Community (EEC) and EURATOM along side ECSC
EEC purpose: to expand customs union to other
goods
elimination of customs
duties
common external tariffs
free movement of labor /
capital
common policies in
agriculture, transport, competition
1962 - Common
Agricultural Policy (CAP)
goals:
improving farmers
living stnds.
reduce overproduction
subsidies and quotas
1968 - customs union in
place
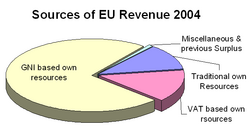
1970 - Financial autonomy achieved through:
Customs duties on imports
Value Added Taxes (VAT)
EU Sources of
Revenue 2004
1970 - regular meetings of foreign
ministers begin

1974 - Summits of Heads of State European
Council begin
1978 - European Monetary
System (EMS)
members start to
coordinate the value of their currencies, limit the range of variation between
them over time

1986 - Single European Act (Delors)
single market/free
trade area
to be in place by 1992
eradicate trade barriers
qualified majority
voting introduced at Council of European Union

1992 - Treaty on the
European Union (Maastricht Treaty)
also called the
Maastricht Treaty because it was negotiated and signed at Maastricht, The
Netherlands, during the Dutch presidency
3 Pillars of the European
Union Enumerated in TEU
1) EECS/EMU
Set
timeline for Monetary Union
European Monetary Institute as of Jan 1 1994 (precursor to
European Central Bank)
convergence of exchange rates
stronger cooperation among central banks
coordination of monetary policies
set
criteria for participation in the currency union
2) Common Foreign and Security Policy (CFSP)
3) Judicial and
Home Affairs
visas, asylum
TEU/Maastricht Treaty also
introduced:
An enhanced role for the
European Parliament
1997 - Treaty of Amsterdam
Four Main Areas of
Emphasis
1. Citizens
Rights
enumerated in the Social Charter
including employment
2. Borders
internal free;
external “ring fence”
3. A Stronger
Voice in World Affairs
4. Decision
Making to be Streamlined
with an eye toward expansion
yet
co-decision still a general rule
Economic and Monetary Union
began with coordination
of exchange rates since 1978
macro-economic
coordination
Currencies to be phased out
by July 2002
Convergence
Criteria:
public debt not to exceed 60% of GDP
deficit not to exceed 3% of GDP
inflation rate within 1.5% of 3 lowest countries' rates
independent central bank
long term interest rates within 2% of lowest 3 countries'
rates
exchange rate fluctuations within normal range (i.e., stable
currency)


The Political Evolution of the EU
From Intergovernmental
Organization
Hallmarks of
Intergovernment EU
unanimous
decision making
strong Commission
weak, appointed
parliament
trade,
competition
To post-industrial Supranational Organization
Hallmarks of Supranational EU
qualified
majority voting
Commission as
executive force "government"
directly elected,
stronger Parliament
trade,
restructuring, currency union, foreign policy, social rights, citizenship
EU Geographic Expansion
1973 - UK, Ireland,
Denmark
(Norway
referendum fails)
1981 - Greece
1986 - Spain, Portugal
1995 - Austria, Sweden,
Finland
(Norway
referendum fails)
2004 - Cyprus, Czech
Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, Slovakia,
Slovenia
2007 – Romania, Bulgaria
Airbus:
An example of European Cooperation in Capital Investment, R&D, and
Production
