Western
European Politcs
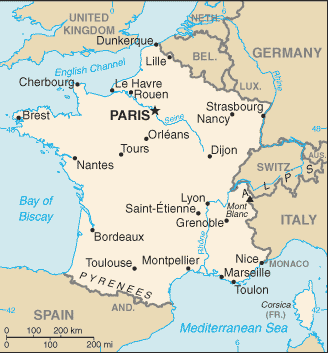
France
Population: 60 mln
Annual
Growth Rate: 0.35%
Rural/Urban
Population Ratio: 24/76
Ethnic
Make-up: Celtic and Latin with Teutonic, Slavic, North African, Indochinese,
and Basque Minorities
Religions: Roman Catholic 83%-88%, Protestant 2%,
Jewish 1%, Muslim 5%-10%, unaffiliated 4%
Life
Expectancy: 75 years (male) 83 (female)
Infant
Mortality: 4.4/1000 live births
GDP Per Capita - PPP: $33,800
GDP Growth
Rate: 1.8%
Inflation
Rate: 1.8%
Unemployment
Rate: 8%
Percent
Population Below Poverty: 6/1%
(2004)
Natural
Resources: coal, iron, ore, bauxite, fish, timber, zinc, potash, arable land
History/Political
Development
Pre-Modern
Through 1200 b.c.
Competition, fighting among the Gauls (related to Celts) and other Germanic
Tribes (e.g., Franks)
Part of the Roman Empire
50 b.c. til 5th Century
Empire built by Charlemagne
800 c.e.
16th Century
Religious wars
Henri of Navarre
Protestant - converts
becomes Henri IV
17th Century
Louis XIV
L’etat c’est moi
18th-20th Century:
major political cleavages
Republicans vs. Monarchists
Catholics vs. anti-clericals
Revolution
of 1789
Louis XVI
Storming of the Bastille
First Republic
1791
Reign of Terror
Constitutional monarchy - 1
yr.
3 more constitutions
Napoleon Bonaparte 1799
1802 - First Empire
Bourbons restored
France
1830 Revolution
New Constitution
Louis Philippe of Orleans
Bourgeois/Urban Revolution
1848
Second Republic (1848-1852)
universal male suffrage
chaos
class conflict (lower/middle)
Napoleon III - 1852-1870
foreign policy
nightmare
Franco-Prussian War 1870
occupation
Paris Commune1871
Lasts only 2 mos.
Est’d by Radicals
Squelched by conservatives
Third Republic
Constitution of 1875 lasts til Nazi
invasion - 1940
Partitocracy
Legislative supremacy
Intense fighting
Catholics/Anti-Clerics
World War II
occupied plus
Vichy Regime- Marshall Petain
colludes with Nazis
de Gaulle - London
“Free French” resistance
Fourth Republic - 1944-1958
constitution nothing new
de Gaulle - resigns after 2 yrs
party politics;
fighting between the “free French” and resistance
Fifth Republic
1958-present
Crisis provoked by
anti-colonial revolt in Algeria
de Gaulle returns from self-imposed
exile; elected president 1958
Constitution written with him in mind for presidency
Dual executive
Strong president
Constitutional council
France - Political Culture
Equality, Liberty,
Fraternity
Distrust in
government/politics
individualism ? anarchism
Addiction to crisis,
upheaval
Craving for order,
authority
Respect for Bureaucracy (equality)
Role of State - etatism
“weighed down by history”
France
Catholicism vs.
Anti-clericalism
79% identify as Catholic
12% attend Mass regularly
67% never or occasional
Revolution of 1789 -
work of Satan or liberation?
Church lands seized
end of estate system
Third Republic (1875 -
1940)
extreme anti-Clericalism
rescinded compact with Church
severed all ties with Church
1879-1939 - no Catholics in Cabinet
violence
Catholics - traditionally right
but not National Front
today more socialists
Islam - France’s second
religion
3 million Muslims
only 27% practicing
Protestants - 1.7% of
population
concentrated in Alsace, Paris, central, southeast
Jews-1.3% of population
shift to N. African Jews
no “Jewish” vote
Separation of Church and State?
Catholic schools subsidized
17% attend
33% of secondary schools are parochial
Constitutional Court ruling
on veils, "religious symbols"
Role of State
Political Institutions
I. Dual Executive
More powerful; "top dog"
Head of State
Was originally a 7-year
term;
but changed to 5-year term in 2000 (2002, 20007, etc.)
re-election possible;
can dissolve Parliament
chooses PM (winning party)
initiates/directs policy
President now?
Nicholas
Sarkozy
Presidential
elections set for 21 April 07 and 5 May 07
2007
Candidates
B. Premier (prime
minister)
head of government/executive
controls administration
ensures executive of the law
govt dismissed by motion or censure or rejection of program
Premier now? Francois
Fillon
Was Jean Pierre Raffarin
from the Liberal Democratic party; appointed by Chirac before May 2002
parliamentary elections (when Jospin resigned) reappointed after elections; resigned
after the vote on the EU constitution (May 2005)
Premier: Dominique de Villepin
since 31 May 05 – May 07
Cohabitation
define
1986-1988; 1993-1995; 1997-2002
Do
the French have a Presidential or Parliamentary System?
C. Council of
Ministers (cabinet)
appointed/removed by President or Premier
chaired by President
forum for deliberation, confrontation
II. The Parliament
A. Lower House
National Assembly
577 members - directly elected
B. Senate
As of 2010, 310 members
Six year terms; Half
elected every 3 years
C. Question Hour weekly
D. Blocked vote -
Parliament
must accept with only Government’s amendments
used to control/discipline the majority
III. Courts
A. Constitutional Council
new with 5th Republic
no tradition of judicial review
power est’d in 1971 decision on prefect’s power to refuse authorization of
associations
Selection.
each president of the two houses chooses 3 members
and President chooses 1
9-year nonrenewable term
no rights of petition for citizens
decision w/in 1 month
no dissents published
rates highly in public opinion
govt consults before introducing legislation
B. Declaration of Rights of Man
Bill of Rights from 4th Republic’s Constitution
France
Role of State/Civil Service
Territorial Divisions
Centralized, unitary system
but some decentralizing reforms 1982-1986
Since 1789
100 departements (4 overseas)
prefect - appointed
with directly elected general, pres council - 6 year terms
Communes - municipalities
mayor, councils elected
6-year terms
New Level of Govt - 1986
Regions - 22 of them
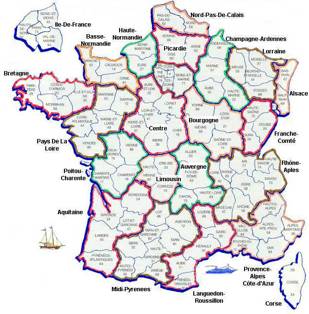
appt’d Prefect
elected assembly, president
6 year terms
Unions
The National Front (FN) (extreme right)
Jean-Marie
Le Pen
Union for a Popular
Movement
successor to Rally for the Republic (RpR)
Chirac created Union in Movement and Union for Presidential Majority in 2002 in
response to challenge from Le Pen
Union for French Democracy
(UDF) (center right)
Valery Gisgard D'estaing
The Socialist Party (PS) (center left)
US- French Relations
