West European
Politics
The Federal Republic of
Germany

People:
Population: 82.4 mln
Population Growth Rate: 0%
Life expectancy: 82 (female); 76 (male)
Births per woman: 1.39
Economy:
Among the world's
largest and most technologically advanced producers of iron, steel, coal,
cement, chemicals, machinery, vehicles, machine tools, electronics, food and
beverages; shipbuilding; textiles
Per capita income: purchasing power parity - $28,700
(2004 est.)
GDP growth rate: 1.4% (2004)
Inflation: 1.6% (2004)
Unemployment: 10.6%
(2004 est.)
Ethnic Make-up:
German 91.5%
Turkish 2.4%
Other 6.1% (made up largely of Greek, Italian, Polish, Russian, Serbo-Croatian,
Spanish)
Religion:
Protestant 34%
Roman Catholic 34%
Muslim 3.7%
Unaffiliated or other 28.3%
I. Political History:
A. Prolonged feudalism;
religious wars between Catholics and Protestants
B. 17th C Prussian Ascendancy
aristocracy,
Junkers
admin efficiency
legalism
Rechtstaat –
state bound by law
militarism
C. Unification 1871
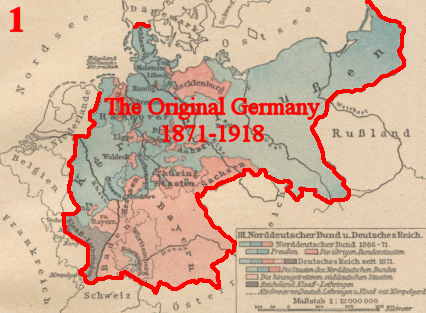
Otto von Bismarck, chacellor
Iron and Rye
coalition
Germany lacked
social modernization – didn’t further it
authoritarian
kaiser retained
taxes/military
service severe
oppressed
Catholics, Social Democrats
D. WWI
militarism -->
economic collapse
blindly obedient
public
Treaty of Versailles,
reparations
loss of
territories
defeated,
exhausted
E. Weimar Republic –
1919-1933
first experience
with democracy
unstable – series
of uprisings
left and right
extremism
economic disaster
and legislative deadlock
1923 – inflation
26 bn%!!!!
Tragic ending
Depression, 1/3
unemployed
Rise of Hitler,
national socialism
F. Hitler
comes to power
through democratic processes
country in
disarray, economic disaster
parliament,
government fails to respond
National
Socialist German Workers’ Party (Nazis)
34% of the vote
in 1932 elections
with Communists
form “negative” majority against
conservatives
Hitler appt’d
Chancellor by President Peter von Hindenburg
G. The Third Reich
(literally the 3rd Empire)
Hitler given
dictatorial powers in response to fire set in Reichstag
“state of
emergency”
all aspects of
society now must be “coordinated” with Nazi goals
opposition
parties suppressed, social and political groups destroyed
violent attacks on Jews,
minorities tolerated, encouraged
economic boycott of
Jewish businesses
Nazi platform
stressed putting
country back to work – public works projects
rebuilt
infrastructure, rearmed in violation of Versailles
H. WWII
Reich conquers
Austria, Czechoslovakia,
Poland, Denmark, Norway, BeNeLux, France, Yugoslavia, Greece
60 mln lives lost
8 million in
genocide; 6 mln of these Jews
May 1945 – Hitler
commits suicide
Europe liberated
throughout 1945 by Soviets from the East and US, UK, Fr from the West
Yalta, Potsdam –
decide new map of Europe
I. Germany
occupied – UK, Fr, US, USSR
losees Eastern
territories to Poland to compensate Poles for giving their Eastern
territories to USSR
Cold War
gradually emerges
II. A Divided Germany
1949-1990
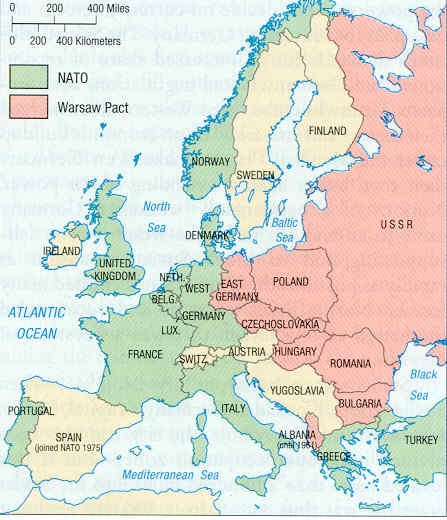
A. The West –
1949 Fed Republic of Germany
Marshall Plan
NATO
European Economic
Communities
Economic Miracle
B. The East – 1949
German Democratic Republic
plundered by USSR
Party of
Socialist Unity (SED)
Council for
Mutual Economic Asst (COMECON)
Warsaw Pact
1961 Berlin Wall
erected
C. 1969-1975 Willi
Brandt and Ostpolitik
apologies;
compensation; recognition
Espionage;
escapes
West German Asylum law
Article 16 of the
Basic Law - broad
persons persecuted on
political grounds shall enjoy the right of asylum; led to other
unintended consequences like the“plane” people – SE Asia; Guestworkers – Turkey
(turks and kurds)
II. German
Reunification
A.liberalization
in Soviet bloc initiated by Gorbachev
Round Table talks
in Poland; elections in Hungary
Hungary opens
border to Austria
Thousands of E
Germans go to Hungary, then Austria
Seek asylum at
German Embassy
B. Regime
embarrassed; announce freedom to travel Nov. 9, 1989
wall opens;
dismantled spontaneously
C. March 1990
first free
elections; CDU wins in East
Sept 1990
Treaty on
Reunification; Basic Law open on Ger territory
D. Commit to parity
of E and W German marks, equal wage rates
Reunification
hugely expensive – tens of billions of dollars
E. Social and
Economic Problems in the East
unemployment
15-35%
per capita income
1/3 to 1/5 of the West
neo-Nazism
alcoholism, drug
abuse
III. Reunited Germany
A. Legacies of
Division
Different Political Cultures
East more secular
more feminist
people accustomed
to state paternalism, econ security
weak dem values
Traditional German
(Prussian) Political Culture
authoritarian,
discipline, obedience, admin efficiency
New (West) German Political
Culture
tolerance, strong
belief in need for political competition/pluralism
strong commitment
to rule of law, protecting civil liberties
B. Religion in
Germany
feudal pd –
prolonged religious wars
home of Martin
Luther; birth place of protestantism
Regional patterns of religious
concentration
Catholic SW
(Bavaria) Protestant N (Evangelical Lutheran)
CDU – embraces both
Catholics and Protestants
Called the CSU in
Bavaria
IV. Institutions
A. Constitutional
Foundation =The Basic Law (1949)
Est’d a Federal system
division of powers
between Federal and Lander (provincial) government
Bund = German for
Federal
16 Lander
control mass media, law
enforcement, education culture, regional planning, administration of national
laws, residual powers (like our reserved powers)
Each Land governed by a
unicameral legislature
Landtag –
directly elected; headed by minister president (like PM)
B. Parliament -=
bicameral
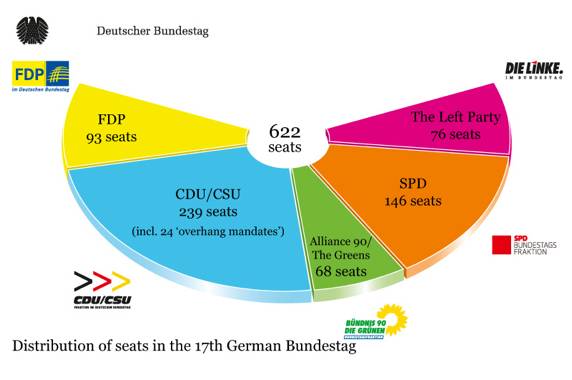
Bundestag
primary legislative
body
amends, evaluates gov’t
legislation
half SMD, half PR
Question Hour
**Constructive
No-Confidence Vote
for vote of
no-confidence to pass in the Bundestag and the govt to be dismissed – must also
propose and vote in a new govt
attempted only
twice; succeeded only in 1982 Schmidt-->Kohl
Party/parties in Government
now?
Grand Coalition between the CDU/CSU
and the SPD
D. Bundesrat
reps Lander at Federal
level
legislation comes here
first but approval only need in areas of concurrent powers (about 2/3 of bills)
appt’d (usually Land
level cabinet members)
6 seats for larger
Lander; 3 for smaller
E. Federal Chancellor
elected by the
Bundestag
cannot dissolve
parliament, call for new elections
“chancellor democracy”
chancellor alone
responsible for policy; ministers must follow his proposals as legally binding
directives
Chancellor now?

Angela Merkel, CDU/CSU
Der Spiegel
story
F. Cabinet
17 dept ministers
appt’d by
President on the rec of the Chancellor
responsiblie for
internal workings of ministry
G. Federal President
mostly ceremonial, head
of state
signs treaties, laws;
appts govt, mil officials, pardons
but with
countersign of the Chancellor
nominates
Chancellor
can call
elections after no-confidence vote lost
selected by Federal
Convention
=Bundesrat members plus
equal number of reps chosen by the Landertag
President now? Christian Wulff
H. Courts
unitary system for
criminal, civil
based on Roman law
principles – codes, abstract
rationalist philosophy
– justice served by following the letter of the law
I. Constitutional
Court
reviews
constitutionality of legis
mediates disputes
between levels of govt
selected in equal
numbers by Bundestag and Bundesrat
can be removed
only for abuse of office
J. Parties
The Greens (a New Left party)
The Left Party
(post-communist successor party)
The Social Democratic Party
of Germany (SDP)
The Free Democrats (FDP)
The CDU/CSU
Extreme Right (under
threshold)
The
nationalist German People's Union (DVU),
The
neo-Nazi National Democratic Party (NPD)
The
Republikaner