
People:
Population: 9 mln – mostly concentrated in southern half of country;
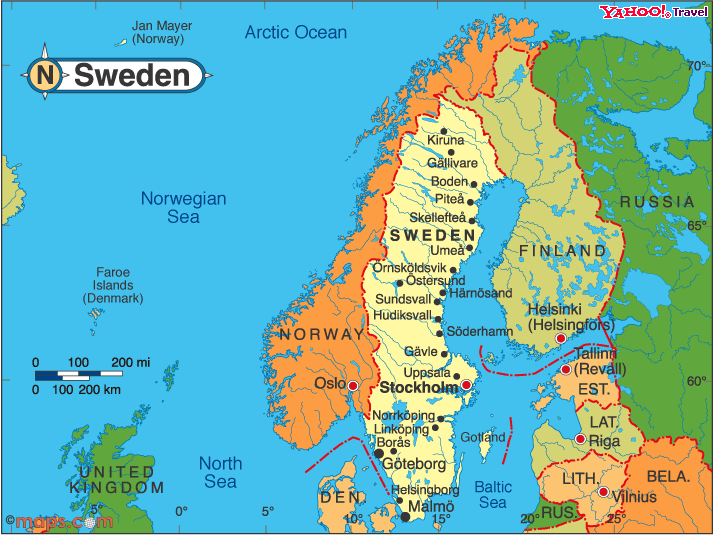


Geography:
Climate: more mild than
latitude would
suggest due to warming winds of the Atlantic, Gulf Stream

People:
Population: 9 mln –
mostly concentrated in
southern half of country;
Population growth: .017% (2005)
Fertility: 1.66 births per woman
Life expectancy: Women 83; Men 78.
Ethnicity:
Traditionally
ethnically homogeneous
but today about 6% of population is
immigrants
Finns,
Yugoslavs, Iranians,
Bosnians,
Norwegians
Turks, Danes, Poles
Religion: 87% Protestant
(Swedish National
Evangelical Lutheran Church);
small
Muslim, Catholic minorities
Economy
Per capita GDP (ppp): $28,400 (2004)
GDP growth: 3.6% (2004)
Average unemployment:
5.6% (2004); 7.2% (1995-99)
GDP generated by sector:
agriculture: 2%
industry: 29%
services: 69%
Broad industrial base
Saab, Volvo, Scania, ABB
Hard to restructure;
slower shift
to service sector
Mergers Saab Aerospace, banking
Success stories-
Ericsson, Tetra-Pak
IKEA
Taxes
Taxes comprise 52% of
GDP (US 28.9;
UK 37.2; Fr 45.2)
(see table p. 356)
Political Culture
mix of conservatism and modernism
secularism
social conformity, care taking
Economically:
“the middle way” between capitalism and
socialism
(not how most Americans would view 50%
personal income tax!!)
Social
compact
rule by small group of wealthy
industrialists,
social democratic technocrats, and trade unions
Welfare State Model
commitment to social equality
consensus politics
corporatism
2006
The model
called into question
Most Politically Salient
History
Viking Conquests thru 9th
Century
Oral tradition, sagas
Legal codification, elected monarchs
Introduction of Christianity, 9th
C
13th C absorbed Finland
Feudal estate system
Landed aristocracy
Clergy
Farmers
15th C Burghers added
Temporarily under Danish rule (along with Norway) 1397
1435 first Riksdag convened; plot rebellion
1521 successful rebellion of
peasants,
miners, nobility
1523 Riksdag elects Gustav Vasa king
(Gustavus
I)
Breaks with Church 1540
16th –17th Centuries
expansionism
controlled large parts of Poland,
Russia
Declines 1709 onward (Russia annexes Finland)
Industrialization
1809 new constitution –
compromise
power shared between kind and four estate
Riksdag
(note again – elected king)
1850s-1890s
pressures from bourgeoisie for liberal
political reform
1889 Social Democratic
Workers Party formed
(SAP)
worked with the Liberals to expand
franchise,
parliamentary government
The Great Compromise of 1901-09 – conservatives conceded universal manhood suffrage in exchange for proportional representation (discuss)
Women get vote in 1918
Political Culture
Respect for constitutionalism and
rule
of law
Veneration of Riksdag
Monarchy as national symbol of unity and
pride (ceremonial roles)
Receptivity to policy innovation, change
Politics of compromise
Moderation, pragmatism
Neutrality, non-intervention
Institutions
Riksdag
Unicameral since 1970 (As in Denmark and
Finland)
Further changes made through acts of parliament Government and Act of Parliament 1973-74.
Both these can be amended by two successive sessions of parliament with an intervening election
1994 reestablished 4-year election cycle for simultaneous national and local elections
Proportional election system,
elected from
24 provinces (multi-member districts)
Must attain 4% threshold in district
or 12% nationally
Interpellations
Remiss procedure – involved interest groups in investigating policy
Top Dog:
Statsminister
(PM)
Elected by Riksdag following popular
election
Note: minority governments possible as
long as not more than half of MPs vote against him/her
Primus inter pares; 17 or so cabinet
members
No confidence votes possible against PM
or individual ministers
Motion to be signed by 10% of Riksdag;
approved by absolute majority
Ombudsman
To investigate complaints against
government; 5,000 per year
Monarchy
Hereditary – just made possible for women
to inherit the throne in 1979-81
Current: King Carl XVI Gustav

Heir: Crown Princess Viktoria
Parties
Socialist Bloc:
*Social Democratic Workers Party (SAP);
usually referred to as the Social Democrats
most successful party since 1932;
for "collective measurwes designed to enhance
individual econmic and social security and the
equality of opportunity" and "economic policies designed to promote
material growth and full employment" (368);
see next
paragraph 368 on emergence of party (instead of liberalism) and
consensual nature of Swedish political culture
The Left Party (VP)
The Environmentalist Party –
the Greens
(MP)
Pre-Greens,
capitalized on concern for
environment; pro-nuclear energy
Center:
The Liberals (Folkspartiet – Peoples’
Party)
Broadly based –
businessmen, workers,
intellectuals, prohibitionists, free thinkers
The Center Party (the former
Farmers’ Party)
Right:
The Moderates (not!)
Second largest vote getters since late '70s
Descendent of
the 19th C conservatives,
who opposed democratization
Tax reductions,
deregulation,
privatization
of education and childcare
Christian Democrats and New
Democracy